The Federal Reserve System (the Fed) is the central banking system of the USA.
US Congress established three key objectives for monetary policy in the Federal Reserve Act:
- maximizing employment.
- stabilizing prices.
- and moderating long-term interest rates.
Fed Organization
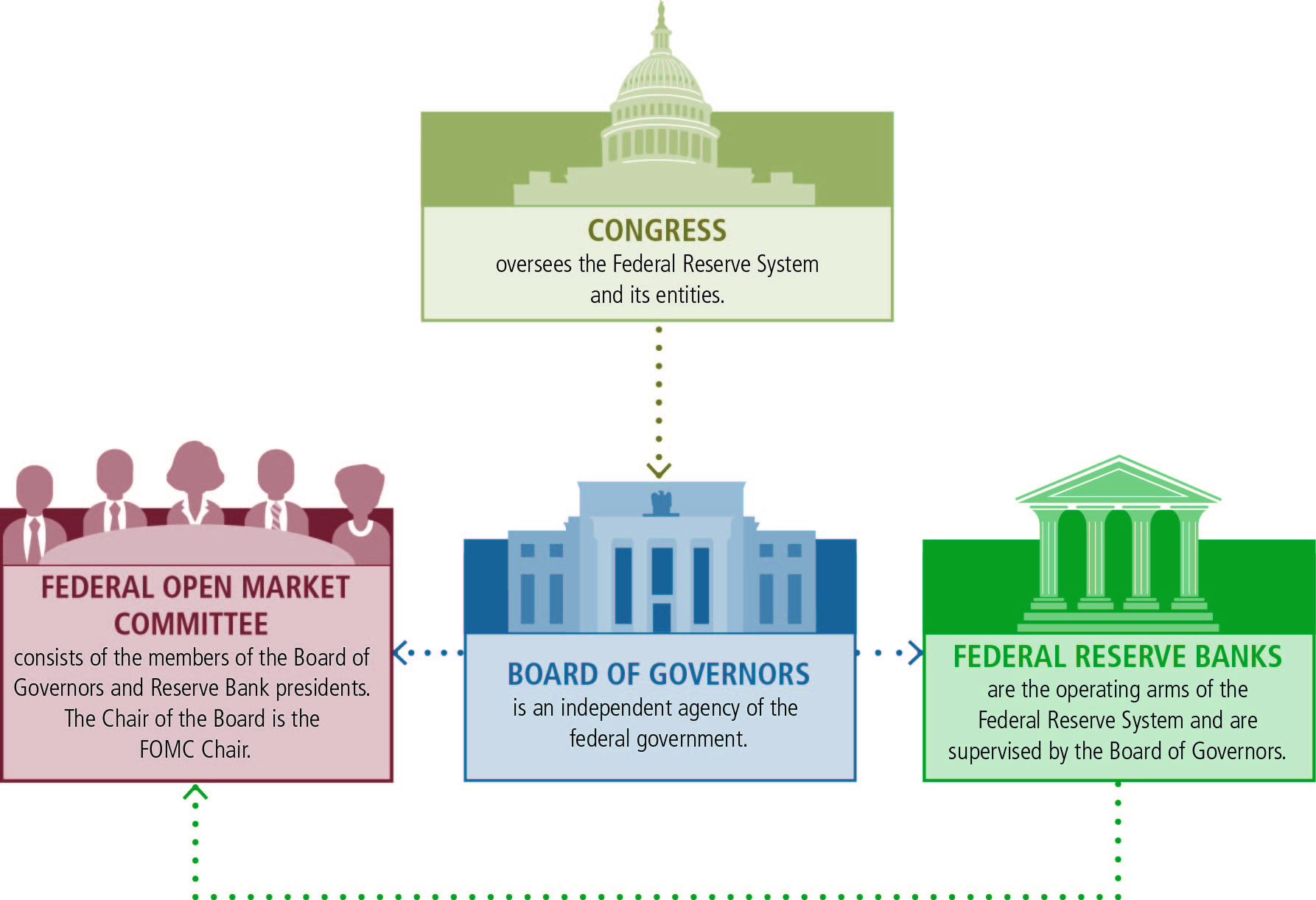
The Federal Reserve was established to serve the public interest. There are three key entities in the Federal Reserve System:
- The Board of Governors,
- The Federal Reserve Banks (Reserve Banks)
- and the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).
The Fed System is governed by the Federal Reserve Board (FRB), an agency of the federal government. FRB reports to and is directly accountable to the US Congress, and provides general guidance for the System and oversees the 12 Reserve Banks.
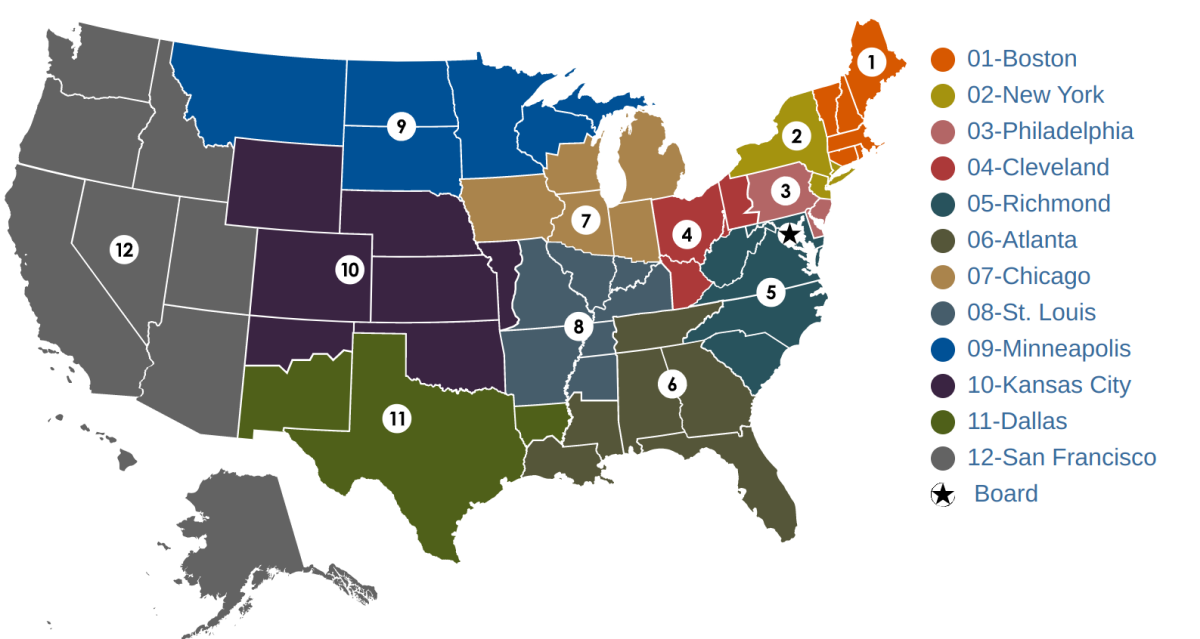
Feds Decentralized System with 12 Districts
In establishing the Federal Reserve System, the United States was divided geographically into 12 Districts, each with a separately incorporated Reserve Bank. District boundaries were based on prevailing trade regions that existed in 1913 and related economic considerations, so they do not necessarily coincide with state lines.
Twelve regional Federal Reserve Banks, regulate and oversee privately-owned commercial banks. Nationally chartered commercial banks are required to hold stock in, and can elect some board members of, the Federal Reserve Bank of their region.
| Federal Reserve Bank | Total assets in millions USD | |
|---|---|---|
| New York City | $4,826,442 | |
| San Francisco | $893,210 | |
| Atlanta | $584,538 | |
| Richmond | $545,399 | |
| Chicago | $618,213 | |
| Dallas | $458,222 | |
| Cleveland | $300,969 | |
| Philadelphia | $179,965 | |
| Boston | $192,866 | |
| St. Louis | $146,484 | |
| Kansas City | $135,711 | |
| Minneapolis | $73,831 |
regulate and oversee privately-owned commercial banks.
The twelve regional banks help make sure the Federal Reserve represents the whole country’s interests, not just those of one central location. This setup ensures that economic and financial information from across the U.S. is included when the Fed makes decisions. Each bank provides a local perspective on economic conditions in its region, which helps the Fed better understand the different economic needs across the country.
Decision-Making Power and the FOMC
Each regional bank’s president participates in the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC), the group responsible for making key decisions on monetary policy, like setting interest rates. The New York Fed always has a voting spot on the FOMC, while the other eleven regional bank presidents take turns voting. This rotation allows the Fed to include a variety of regional perspectives in its decisions.
Federal Reserve Board of Governors (FRB)
FRB consisting of 7 people who are appointed by the US President, and then approved by the Senate for 14 years without the right to renew their powers, while every two years one of the members of the Council is replaced. This is done in order to enable the Board to act consistently, have competent members, maintain independence, or autonomy.
Jerome Powell (member of Republican Party) is the current Chairman of the FRB

Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC)
The FOMC is the body of the Federal Reserve System that sets national monetary policy. The FOMC makes all decisions regarding the conduct of open market operations, which affect the federal funds rate, the size and composition of the Federal Reserve’s asset holdings, and communications with the public about the likely future course of monetary policy.
FOMC consists of all seven members of the board of governors and the twelve regional Federal Reserve Bank presidents, though only five bank presidents vote at a time. The president of the New York Fed and four others who rotate through one-year voting terms. All 12 of the Reserve Bank presidents attend FOMC meetings and participate in FOMC discussions, but only the presidents who are Committee members at the time may vote on policy decisions.
By law, the FOMC determines its own internal organization and, by tradition, the FOMC elects the Chair of the Board of Governors as its chair and the president of the Federal Reserve Bank of New York as its vice chair.
FOMC meetings typically are held eight times each year in Washington, D.C., and at other times as needed.
Open Market Trading Desk
The Open Market Trading Desk (the Desk) at the Federal Reserve Bank of New York (New York Fed) is responsible for conducting open market operations under the authorization and direction of the Federal Open Market Committee (FOMC).